Which Hungarian political parties use Facebook most successfully to create and engage with a significant online following? A comprehensive effort to find out reveals two things: the balance of forces between the Hungarian parties on Facebook is very different from what the actual results of the elections in April will be like – and despite what is basically a three-party system in real terms, there are a lot of Hungarian political parties with a Facebook presence.
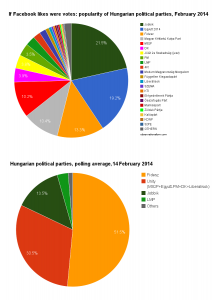
Facebook likes vs current polling for Hungarian parties
The chart on the right (click to enlarge etc., and yes, it’s a pie chart – but if that makes you twitch, there’s a bar chart further down this post) specifies the 22 parties with the largest numbers of fans. For comparison’s sake there’s a chart representing current opinion polling data underneath.
I’ve taken the concept of “parties” in a light spirit and included the satirical Two-Tailed Dog Party (which once again has been denied registration, so it can’t take part in the elections this year), and it happens to blow many of the regular parties out of the water. (On that note, the Fourth Republic party 4K! probably also enjoys an unfair advantage, since it might now be seriously campaigning as an alternative left-wing party, but it used to be better known on Facebook for organizing things like an annual pillow-fight event.)
So who wins the Facebook races?
That would be the populist, far-right Jobbik party, best known for its rhetorics against “Gypsy crime” and recurrent bouts of anti-semitism. It is ‘liked’ by a whopping 188 thousand people on Facebook. Jobbik is especially strong among young voters, so its prominent showing on Facebook is no surprise, though the fact that it beats out all the other parties may be more of a shock. In the 2010 elections, Jobbik received 17% of the vote, and right now it’s polling at about 13%, so it’s a significant force in the real elections as well, but will remain deep in the shadows of the governing Fidesz-KDNP alliance in the elections.
Right behind Jobbik is Together 2014, the movement launched around former Prime Minister Gordon Bajnai, which for some time from late 2012 on roused the hopes of a center-left, liberal, pro-EU electorate for a strong new opposition force. The movement largely fizzled out though, and is now taking part as the largest junior partner in the five-party, left-of-center “Unity” opposition alliance under the leadership of the Socialist Party’s Attila Mesterházy. Together 2014 does almost as well as Jobbik on Facebook, which surprised me – but only in quantity of likes, not in actual engagement, as I’ll show below.
Third place is for Fidesz. All-powerful as it may be in the Hungarian state, government and, dare one say, economy (as well as current election polling), it doesn’t even get to play second fiddle on Facebook. Or does it? Fidesz may have ‘only’ 116 thousand or so likes, Prime Minister Viktor Orban has 219 thousand. Bajnai, in comparison, only has 103 thousand, and Jobbik’s Gábor Vona 155 thousand.
Coming in fourth is … no, still not the Socialist Party. It’s the Two-Tailed Dog Party, which promised such goodies as free beer, eternal life and “more of everything, less of nothing” in its previous abortive attempt at joining electoral politics. The Socialists only have 89 thousand likes – an unsurprisingly weak performance for a party best known for its legacy support among stubborn pensioners. Though Mesterházy himself does significantly better, with 152 thousand likes.
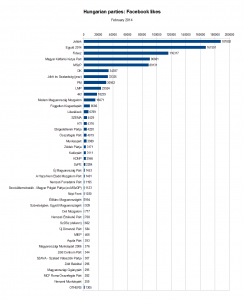
All Hungarian parties with more than 250 likes on Facebook
The rest of the parties follow at a respectful distance. The most popular of the lot include former Prime Minister Ferenc Gyurcsány’s Democratic Coalition, with 34 thousand likes (though his own page does much better, clocking in at almost 89 thousand) and the green party Politics Can Be Different (LMP), with 24 thousand.
The latter is outdone by two others though. The LMP broke up acrimoniously last year, and the break-away fraction formed “Dialogue for Hungary” (PM), which swiftly joined Together 2014 and, now, Unity. And on Facebook, PM easily surpasses LMP with 31 thousand likes. Even more surprisingly, both have fewer Facebook likes than the Welfare and Freedom Democratic Community (JESZ), which was founded upon the ashes of the once-important Hungarian Democratic Forum.
Honourable mentions go, not just to Fourth Republic, but also Lajos Bokros’s Modern Hungary Movement (16 thousand likes) and … the Independent Smallholders Party. They still exist! “Újra erősek vagyunk!”, We Are Strong Again, their posters exclaim somewhat optimistically, and hey – they do have more likes than any of the three liberal parties that emerged from the wreckage of the Alliance of Free Democrats. (Which reminds me: does Hungary really need six different green parties?)
The largest party, on Facebook at least, that I had never heard of is the Elégedetlenek Pártja, i.e. the Party of the Discontented. Which seems fitting. And if you think that the parties at the bottom of this second chart, which are mostly of the far-right, far-left, ecological and Romani varieties, are doing rather pathetically with just a couple of hundred likes, trust me – it can be much worse. After doing Facebook searches for every party I came across trawling through the Hungarian Wikipedia’s list of parties, the list of parties that registered a willingness to take part in the last elections and, last but not least, the decisions handed down by the National Elections Commission so far this year, I’ve found a total of 60, and the smallest one has just 13 likes. There are actually 15 different parties with fewer than 100 likes – don’t these people have friends and families to rope in? Here’s the full list – with URLs.
UPDATE: Active followers vs. disengagement and ‘fake’ likes
There are of course a lot of ways to artificially boost the numbers of likes for your page. Paying Facebook for ads is the simplest way. If you want to break the rules, you can also pay clickfarms for thousands of extra likes, though many of them might then come from South- or East-Asia. A friend pointed me to some evidence that a couple of Jobbik politicians took a more convoluted road. At least that’s what a blogger appeared to find out, when he followed a link to some clickbait story on a Hungarian site called DailyStory, was asked to ‘like’ the site to see the content, clicked ‘like’, and afterwards went back to his Facebook profile to erase the ‘like’ again. Turned out he hadn’t just liked anything from DailyStory, but instead the Facebook page of a Jobbik MP. A look at the page source of the DailyStory item confirmed that they’d actually pointed the ‘like’ to Mr. Lajos Kepli’s page, and some further digging revealed that the owners of DailyStory also own a site called “LikeMarket”. Looks like Mr. Kepli, and at least one other Jobbik politician, used that site’s services …
Does that mean that none of the numbers in this blog post can be trusted? Or that the Jobbik page’s numbers are probably bogus? I don’t think so, and not just because the revelations were only about a couple of individual politicians.
Of course it’s always good to be skeptical about page likes as stand-alone metric. If you want to review an entity’s success in engaging supporters on Facebook more properly, you should look beyond those, for example at how many likes, shares and comments individual posts get, or how many people click on the links on the page. Since people who were tricked in liking a page or got paid for it by a clickfarm aren’t likely to start actively commenting on it, that also helps to weed out the fake “likes”. Of course all of that goes far beyond the scope of a blog post, but Facebook does provide a straightforward alternative metric: “Talking about this”.
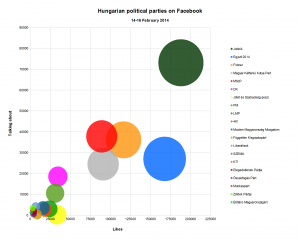
Likes versus 'Talking about it': how engaged are the FB followers of the different parties?
This metric measures how many people have, in the past week, commented on, shared or liked a post, joined an event, mentioned or checked in at a page, etc. Since it still includes new page likes too, it doesn’t wholly do away with the problem, but it helps. So how do the Hungarian political parties do when comparing total page likes and “people talking about this”? The chart’s on the right!
Turns out, Jobbik still rules the roost. Both in page likes and people ‘talking’ about their page. Their conversion rate of likes into actual engagement is actually better than most of the other parties are doing – suggesting no evidence of massive numbers of ‘fake’ likes distorting their top line number.
Instead, it’s Together 2014 which has a very low conversion rate, which is why it’s drooping towards the bottom right of the chart. Evidence that Together 2014 has fake likes? Not hardly, because many other things can explain such disengagement on the part of the ‘likers’ too. A feeling of resignation, for example, or disappointment. Together 2014 roused a fair bit of hope among center-left and liberal opposition supporters when it was launched – but a lot of those people are presumably not particularly enthusiastic by the new “Unity” alliance which Together 2014 has joined, led as it is by the Socialist Party and burdened by its inclusion of the very divisive politician Ferenc Gyurcsany and his Democratic Coalition.
Wholly anecdotically, I can say that 17 of my friends turn out to ‘like’ the Together 2014 page, more than any other party except the Two-Tailed Dog Party (which I guess tells you something about my friends) – and I know that many of them don’t trust Gyurcsany and/or the Socialists (who have a solid base but are perceived as corrupt, inept ex-communists even by many liberals and greens). There really doesn’t seem to be any enthusiasm about these elections – it’s all resignation about the inevitability of a Fidesz victory and the unattractiveness of the opposition.
It’s therefore interesting to see which other parties are showing higher or lower engagement rates among their Facebook followers. Higher than most? The Democratic Coalition and, to a lesser extent (roughly at a par with Jobbik), the Socialist Party. A sign that the old-fashioned polarization of the election campaign is rallying the base of the traditional left, at the same time (and for the same reasons) as it is depressing engagement among those who feel alienated from the old politics? Just like Together 2014, the green Politics Can Be Different party is doing weakly as well, burdened by last year’s split and its gloomy prospects of making it back into parliament.
Among the small parties, followers of Fodor’s Liberálisok do seem very engaged, and to some extent those of the KTI are too. Those of 4K!, many of whom probably came for pillow fights rather than politics, are not. The center-right JESZ, belying its relatively high number of page likes, is getting hardly any interaction at all – over 33 thousand likes, but just 205 people ‘talking about it’, that’s a horrible engagement rate. Then again I don’t think they’re taking part in the elections. Among the tiny parties, two itty-bitty green parties, the Zöldek Pártja and Élőlánc Magyarországért, have proportionally high ‘Talking About This’ numbers.
Age appeal
Finally, one thing is true for most of the political parties: people who ‘like’ a party are old, especially in the context of Facebook. As in: between 55 and 65 years of age. The notable exceptions are Jobbik, LMP, 4K! and, surprisingly, the KTI and Jesz. (Really? In combination with the horrible engagement rate, you’d almost think it’s JESZ which bought some likes …). Here are the numbers, according to Facebook, right now:
|
|
|
|
|
. |
Party
| Most pop. age group |
|
. |
Jobbik
| 18-24 |
|
. |
Together 2014
| 55-64 |
|
. |
Fidesz
| 35-44 / 55-64 |
|
. |
Two-Tailed Dog Party
| 18-24 |
|
. |
Socialist Party
| 55-64 |
|
. |
Democratic Coalition
| 55-64 |
|
. |
JESZ
| 18-24 |
|
. |
PM
| 55-64 |
|
. |
LMP
| 25-34 |
|
. |
4K!
| 18-24 |
|
. |
Modern Hungary Movement
| 55-64 |
|
. |
Independent Smallholders
| 35-44 / 55-64 |
|
. |
Liberals
| 55-64 |
|
. |
SZEMA
| 55-64 |
|
. |
KTI
| 18-24 |



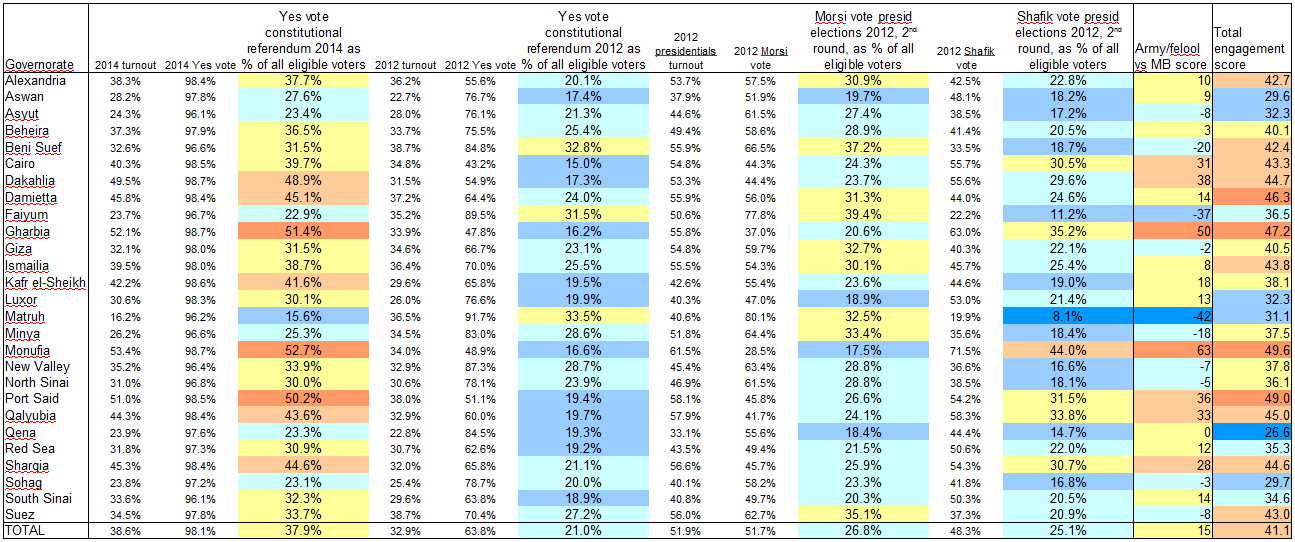
![Egypt: "regime vs MB" score by governorate Egypt: "regime vs MB" score by governorate [Map]](http://observationalism.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/egypt_regime_vs_MB_score-300x300.png)
![Egypt: "Engagement score" Egypt: "Engagement score" [Map]](http://observationalism.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/egypt_engagement_score-300x300.png)

 As you’ll have guessed, that was the Minnesota race between Al Franken and Norm Coleman. The two men raised $20.5 million and $18.0 million, respectively. That translates to $488 thousand and $430 thousand for each percentage point of the vote they ended up winning – which ranks Al and Norm as #1 and 2 when it comes to raising the most money per percentage point won.
As you’ll have guessed, that was the Minnesota race between Al Franken and Norm Coleman. The two men raised $20.5 million and $18.0 million, respectively. That translates to $488 thousand and $430 thousand for each percentage point of the vote they ended up winning – which ranks Al and Norm as #1 and 2 when it comes to raising the most money per percentage point won. Your vote was worth most up in Alaska. Mark Begich raised a total of $4.4 million – which translates to a royal $29 for every single vote he received. His opponent, Ted “bring home the pork” Stevens, was right up there too and raised a stunning $26 per vote – in vain.
Your vote was worth most up in Alaska. Mark Begich raised a total of $4.4 million – which translates to a royal $29 for every single vote he received. His opponent, Ted “bring home the pork” Stevens, was right up there too and raised a stunning $26 per vote – in vain.


