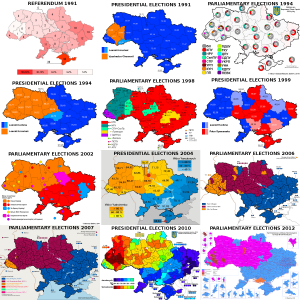
As Washington Post blogger Max Fischer illustrated with what he called “the one map you need to understand Ukraine’s crisis”, the current protests and revolts in Ukraine are fierce, but largely limited to the north and west of the country, which is right in line with the pattern revealed in the 2010 election outcomes. It’s no secret that the same broad geographic divide appeared, time and again, in most of the elections since 1991, when Ukraine gained independence.
For convenience’s sake, I gathered electoral maps for all the presidential and parliamentary elections in those twenty years (as well as the 1991 independence referendum), in one big overview file. All of those maps are from Wikimedia/Wikipedia.
(One contestable editorial decision I made for the 2012 parliamentary elections was in choosing the map that showed the leaders in multi-member districts by constituency, rather than the one showing the leaders in single-mandate constituencies, which includes a lot of independents and is therefore less clear. I also couldn’t find a map of the results for Gorbachev’s All-Union referendum in 1991.)
Oddly, the candidates actually running for presidential office sometimes seemed irrelevant to the geographic divide itself. In 1991, the former dissident Viacheslav Chornovil was the worthy but politically weak candidate who won only in the Galician northwest of the country, while former apparatchik Leonid Kravchuk based his landslide victory on wide support in the south and east. But in 1995, the roles were reversed: Kravchuk won constituencies across the north and west when he lost his reelection bid against Leonid Kuchma, who swept the vote in the south and east. Those elections marked the first real time that the electoral map showed a dividing line right down the middle of the country that would start marking election maps again in every major election after 2002. But it gets stranger still: move on to 1999, when Kuchma faced a Communist Party candidate as opponent in his reelection bid — and it was Kuchma who won almost all of the north and west, while support for the communist candidate was based mostly in the south and east.
Considering Chornovil’s, Kravchuk’s and Tymoshenko’s losses, and the gritted teeth with which many voters in Kiev and the northeast must have voted for Kravchuk in ’94 and Kuchma in ’99, it’s hard to elide the thought that this pattern illustrates how the real political power in the country has lain in the south/east. The voters in the north/west have had to choose between voting for the lesser evil or rebelling in the streets. Yushchenko’s victory would be the only exception, and that took a revolution. I doubt that Viktor Yanukovich will ever switch to being the northwest’s candidate, though …
There is one further geographic wrinkle of note in these maps, and that is how the Transcarpathian/Ruthenian region constitutes a bit of an outlier within the northwestern half of the country. That’s the region midway on the left side, where the country’s borders take a turn east to curve around Romania, which is often coloured differently from all the surrounding territories. It can’t be a coincidence that the historical background of that region is wholly separate. Whereas the rest of northwestern Ukraine used to belong to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, and much of it to interbellum Poland as well, this region belonged to the Austro-Hungarian empire until WW1, and to Czechoslovakia between the two world wars.
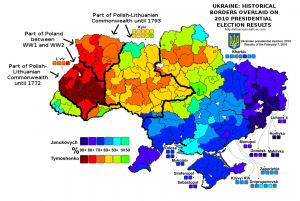
When it comes to elections, history can be destiny. A map overlaying the borders between Imperial Russia and Imperial Germany on the Polish election results of 2007 has done the rounds online among map geeks for a few years because of the striking correspondence it reveals. And on a Reddit thread about these Ukrainian election maps, commenter Martin Keegan pointed out that “the boundary is where the old Polish-Lithuanian – Russian border used to be,” an idea he previously proposed on his blog. That piqued my curiosity, so I ventured on an effort to do a similar overlay to the Polish one: how do the old Polish and Lithuanian borders with Russia overlap with Ukraine’s current political polarization?
It was more of an effort than I’d have thought. But here is the result, overlaying different historical borders on the 2010 Presidential election results. It turns out that Keegan wasn’t entirely correct about the old Polish-Lithuanian – Russian border – but he definitely had a good point about the continuing salience of historical borders. Check out how the territory that still belonged to Poland in between the two world wars overlaps with the most overwhelming support for Tymoshenko (click the map to enlarge).
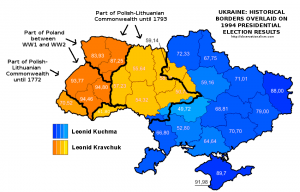
Moreover, Keegan’s point appears more vindicated when looking at the 1991 referendum results, though the division there was merely one between a large versus a near-unanimous majority in favour of idependence, or, especially, the 1994 presidential elections. Here is what the historical overlay looks like for the latter:
There are, however, also ways in which history is conspicuously not destiny. Or at least not in ways that are immediately obvious or make sense intuitively. Check out this map of the Holodomor – the genocidal, man-made famine that struck large parts of Ukraine, which is often blamed on indifference or outright malice on the part of Stalin and his regime. Compare it with the post-independence electoral maps, and any overlap is … hard to see. If anything, the Holodomor was most devastating in areas that now habitually side with Russia-friendly politicians like Yanukovich. Which doesn’t immediately make instinctive sense.
Methodological note:
The historical borders are approximate, though I did my best to be precise. As source material I used a map of Northeastern Europe around 1700; a Wikimedia map of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth anno 1789; a Wikimedia map of Poland after the Second Partition of 1793; the detailed 1794 Laurie and Whittle map of the Kingdom of Poland; and an administrative map of Interbellum Poland in 1930. In addition, I used the Wikipedia page and subpages on the administrative raions of Ukraine, and a detailed Ukrainian Wikimedia map of the electoral multimandate raions of the country. Delineating the far eastern border of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth was a bit difficult since some settlements like the erstwhile Krylov that were right on the border back then have long been submerged in the Kremenchuk dam reservoir. In the south, the problem in defining how the historical border overlaps with current territories, lacking more detailed maps, lies with the transfer of Transnistria to Moldova.
![Egypt: "regime vs MB" score by governorate Egypt: "regime vs MB" score by governorate [Map]](http://observationalism.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/egypt_regime_vs_MB_score-300x300.png)
![Egypt: "Engagement score" Egypt: "Engagement score" [Map]](http://observationalism.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/egypt_engagement_score-300x300.png)