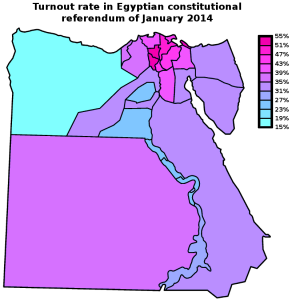
Last Sunday, Egypt’s Supreme Electoral Committee announced the results of the referendum on the new constitution: no less than 98.1% of Egyptian voters had cast a vote in favour of the new text. That Eastern Block-style result should, however, be placed in the context of a turnout of just 38.6% — surely a less resounding affirmation of the new regime than the army would have hoped. Turnout reached up to 51-53% in the governorates of Menofiya and Gharbiya, in the Nile Delta, and Port Said; but it stayed under 24% in the governorates of Matrouh, Fayoum, and upriver in Sohag and Qena.
How does this result compare with the turnout and “Yes” vote in 2012, when it was the Muslim Brotherhood government that was pushing through a constitutional referendum? In addition, what does the turnout map reveal about the political geography of Egypt? The current referendum was of course boycotted by the Muslim Brotherhood, as well as by the most radical of the revolutionary groups, the April 6 Movement. The April 6 Movement is relatively small, however, and the constitution was supported by many other liberal and radical groups (and the extent of popular support for the liberal and leftist groups is in any case in doubt). So were the areas of low turnout correlated to areas of high support for the Muslim Brotherhood?
The trick in comparing the results of this year’s referendum with the one two years ago is that you’re dealing with two separate elements: the turnout, affected as it might be by boycotts and apathy, and the percentage of actual “Yes” voters. This year, turnout was low, at least by international standards, but almost everyone who went out to vote, voted “Yes”. (Considering the current climate of repression, opponents might also not have dared to come out to vote “No”). However, in the 2012 referendum turnout was even lower, at 32.9%, and in addition, there was a substantive number of people who came out only to vote against the Muslim Brotherhood’s constitution.
To take account of both elements, in the table below (click for full size), I’ve taken the turnout and “Yes” vote percentages in each referendum and calculated the number of “Yes” voters as percent of all eligible voters. I also did the same for the results of the second round of the 2012 presidential election, when Brotherhood candidate Mohamed Morsi faced off against Ahmed Shafik, widely associated with the ancien regime, army and “felool”.
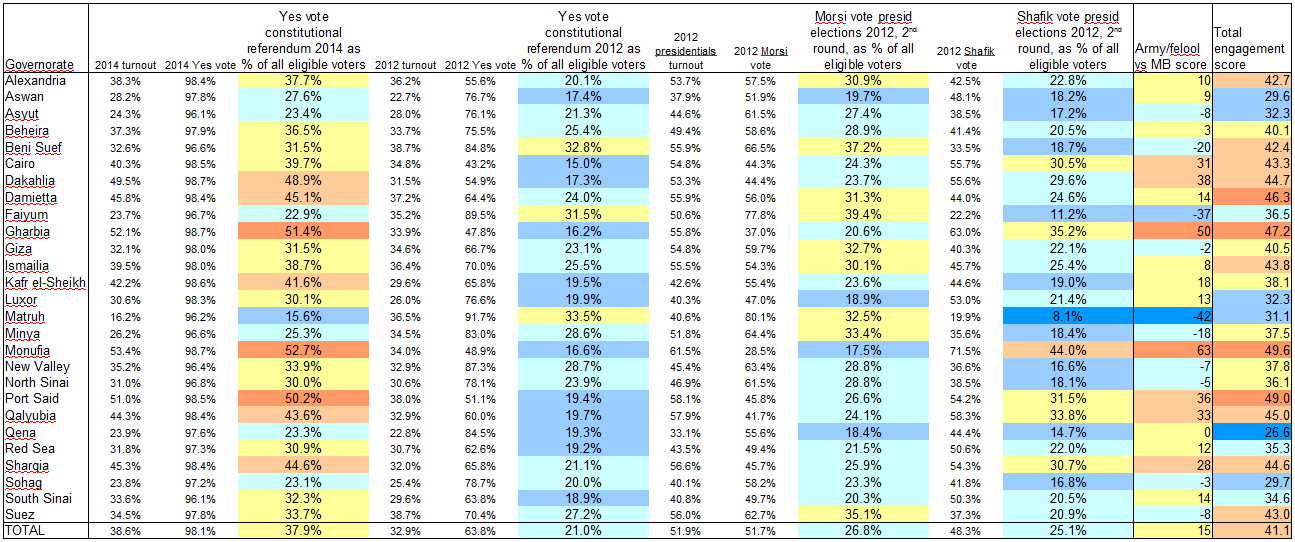
The constitutional "Yes" votes of 2012 and 2014 and the 2012 presidential election results (second round) in comparison, taking into account turnout rates
In short, especially when you take turnout into account, the army’s referendum this year fared much better than the Brotherhood’s proposal two years ago. Then again, context is important. The army inundated the airwaves and streets with propaganda, whereas even just carrying flyers against the constitution could get you harassed or arrested. Morsi’s government was repressive in its own ways, but the campaign back then wasn’t anywhere as one-sided, with the opposition holding public rallies in Tahrir Square and elsewhere. The direct comparison in this table shouldn’t therefore be taken simply at face value. One thing it can be useful for, I think, is to identify local and regional electoral patterns.
In the table above, I added two extra columns at the right end, based on formulae that I freely made up on the spot. I rather crudely labelled the first one the “Army/felool vs MB score”, which I know overly simplifies things. The formula is very straightforward:
Yes vote 2014 as percent of eligible voters + Shafik vote as percent of eligible voters - Yes vote 2012 as percent of eligible voters - Morsi vote as percent of eligible voters.
![Egypt: "regime vs MB" score by governorate Egypt: "regime vs MB" score by governorate [Map]](http://observationalism.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/egypt_regime_vs_MB_score-300x300.png)
"Regime vs MB" score: The Yes vote in the 2014 constitutional referendum and the Shafik vote in the 2010 presidential elections, minus the Yes vote in the 2012 constitutional referendum and the Morsi vote in the 2010 presidential elections (all as percent of all eligible voters)
On the other hand, by this calculation, Monufia and Gharbia are by far the strongest army/establishment bulwarks, but Dakahlia, Port Said, Qalyubia, Cairo and Sharqia all rank highly here too.
There is another, less obvious dimension of these results though, which interested me when I noticed that the people of Aswan, Qena, Sohag and Luxor appear to not have particularly liked any of the choices. In these governorates, both the “Yes” vote in 2012 and that of 2014 (as percentage of all eligible voters) stayed below the national average. And turnout in the second round of the presidential elections there was low enough that both Morsi and Shafik failed to reach their national average score, as percentage of all eligible voters. That’s why I added that last column in the above table. I dubbed it the “engagement score”, but it’s really nothing more than just the average turnout in the three elections.
![Egypt: "Engagement score" Egypt: "Engagement score" [Map]](http://observationalism.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/egypt_engagement_score-300x300.png)
Average turnout in the second round of the 2012 presidential elections, the 2012 constitutional referendum, and the 2014 constitutional referendum
The correlation between the two above maps also suggests a strategic problem for the Muslim Brotherhood (though it is obviously more concerned with more immediate threats at the moment). Most of the governorates where the army/regime appeals least, judging on the 2014 results and Shafik’s 2012 result, also seem to be among the lesser-energized governorates overall, which weren’t particularly motivated to turn out by either of the two sides in these elections/referenda.
After all, Faiyum, Matruh and Minya didn’t just massively boycott the 2014 referendum; in 2012 turnout there was barely over the national average, and in the 2012 presidentials Morsi can’t have inspired them too much either, because turnout was either just around the national average or, in the case of Matruh, much below it. (Beni Suef is the exception, with an above-average ‘engagement score’).